Nitrite is converted from nitrate, so the nitrate content in vegetables is closely related to the nitrite content. Plant nitrates, which are increased due to the absorption of nitrogenous fertilizers (nitrogen fertilizers), are mainly concentrated in the young tissues of plants, while mature seeds are free of nitrates because in the mid-to-late stage of plant growth, inorganic nitrogen (such as nitric acid Salt) is converted into organic nitrogen such as proteins and nucleic acids and stored in seeds. The survey found that about 80% of the dietary nitrates and nitrites came from vegetables, and the remaining 20% ​​came from drinking water and other foods. The edible parts of plants that serve as plant vegetative organs (leaves, stems, and roots), such as spinach, celery, cabbage, radish, and lettuce, have high levels of nitrate, and the edible parts are plant reproductive organs (flowers, fruits, Seed) vegetables, such as cauliflower, cucumber, eggplant, green pepper, soybean meal, etc., have low nitrate content.
In addition to the types of vegetables, the following factors increase the nitrite content in vegetables:
1 pickled vegetables, mainly short-term pickled vegetables contain more nitrite. The nitrite content will increase significantly when spoilage or moulding occurs due to poor pickling conditions or excessive pickling time. In the pickling process of vegetables, the content of nitrite is minimized within 4 hours of soaking. Nitrate is then converted into harmful nitrite by some bacteria. It reaches peak quickly (3 to 14 days). Nitrate is gradually being used by bacteria or broken down into other nitrogenous substances. (30 days later) Nitrite in pickles will gradually decline to a lower level or even disappear. Therefore, the nitrite content of vegetables that have been preserved for more than one month is rather low (except for rot and mildew).
Therefore, when marinating vegetables, marinate and eat, and avoid mold and mold. In addition, when pickling vegetables, adding onion, ginger, garlic, and pepper sauce all help reduce the nitrite content. Vitamin C can also block nitrosamines from synthesizing carcinogen nitrosamines.
In general, it is safe to produce foods that are scientifically produced, marinated for a long time, and free from mold and spoilage. It should be noted that, compared with fresh products, pickled vegetables have large losses of nutrients and high levels of salt. From the point of view of nutrition, they are far better to eat fresh vegetables. Therefore, the “Chinese Dietary Guidelines 2007†recommends pickling. Vegetables and pickles should be eaten less.
2 Long-term storage? Among the fresh vegetables just harvested, the nitrite content is very low, but under the action of self-enzymes, the nitrite content will gradually increase with the prolonged storage time. Vegetables stored at room temperature for 1 to 3 days, the nitrite reached a peak; refrigerated conditions, peaked at 3 to 5 days. For green leafy vegetables such as spinach and pakchoi, the production of nitrite is particularly large, and the effect of refrigerator storage is much better than that at room temperature. For cucumbers and potatoes, the difference is not obvious. However, after several days of storage, the contents of nitrate and nitrite in Chinese cabbage decreased. This may be due to nutrient depletion during storage and conversion to other nitrogenous substances, so there is no need to worry about the nitrous acid in winter storage cabbage. Salt problem. After the vegetable is spoiled, the nitrite content is greatly increased under the action of bacteria and should be avoided.
Vegetables are always fresh and, when conditions permit, they should not eat vegetables that have been stored for too long, are not fresh, or have begun to spoil.
3 Leftovers (refers to unfinished vegetable dishes) After the vegetables are cooked, their enzymes are killed, but bacteria grow in size, and many bacteria are able to produce nitrate reductase, which converts nitrate into Nitrate increases the nitrite content in leftovers.
Keeping the leftovers in the refrigerator at low temperatures is a good way to suppress bacterial growth and reduce nitrite production. However, it must be put in the refrigerator just after the vegetables are cooked and the number of bacteria is still low. If the dishes have been turned on the plate with chopsticks for a period of time, large amounts of bacteria have been infested, and even if placed in the refrigerator, it is not safe. The longer the storage time at room temperature, the more the number of flips, the more bacteria will multiply. Reheating the leftovers before eating can kill the bacteria and avoid bacterial food poisoning, but it still cannot destroy nitrite. Therefore, even if placed in a refrigerator, the leftovers should not be stored for more than 4 to 6 hours. It is best not to eat leftovers that exceed this storage time.
· Made of pure PP and widely used in molecular biology, clinical chemistry and biochemistry research
· The pipe cover and the pipe body are polypropylene
· Black or white screen printing scale, large area of white mark area
· One-handed operation, easy to spin tube cover, good sealing
· Up to 12000xg centrifugal force
· Bearable temperature range-80 c-120 c
Medical grade polypropylene material
Ultra-thin tube wall, extremely fast temperature conduction; pipe transparent, easy to observe
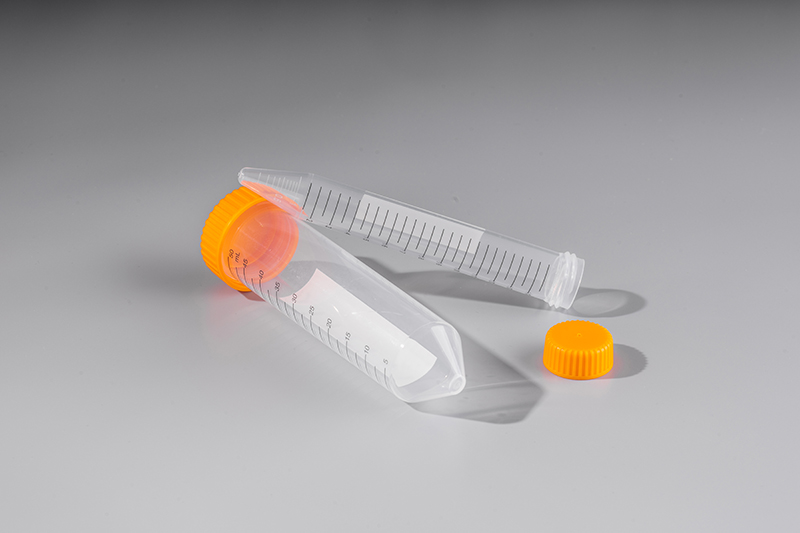
Centrifuge Tube,Micro Centrifuge Tubes,Screw Centrifuge Tube,Polypropylene Centrifuge Tubes
Jiangsu iiLO Biotechnology Co., Ltd. , https://www.iilogene.com