First, the introduction
Research and drug development of targeted cells cannot avoid the analysis and tracking of cell viability. However, depending on the final purpose of the experiment and the parameters of interest, the cell viability will be reflected in different methods. For example, cell proliferation assays are useful for comparing the proliferative capacity of different cell lines, while cytotoxicity assays can be used to explore whether a candidate drug is cytotoxic. From the analysis instrument, the current mainstream detection platforms, such as microscope, flow cytometry and real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR instrument, can be used for cell viability analysis, but the indicators, sensitivity and flux of different platforms will be The difference is therefore the need to select the appropriate detection platform based on the biological questions and indicators answered. In the above platform, the microplate reader provides a high-throughput cell viability assay for 96- and 384-well plates, which is comparable in sensitivity to the classical [3H] Thymidine Incorporation Assay. Cell viability and toxicity analysis platform for research and industrial R&D. Correspondingly, cell viability analysis has become one of the basic applications of microplate readers and is the main application of Molecular Devices (MD).
In this manual, we will introduce you from the microplate reader, compare the mainstream cell viability, toxicity analysis methods, and show you how to use the MD microplate reader and software to easily and professionally complete cell viability through detailed application materials. , toxicity analysis.
Click to download the full version of the application manual
Click to download the full version of the application manual
Second, cell viability analysis
This section focuses on common cell viability assays such as MTT and ATP. Although these assays are also commonly used to analyze drug toxicity and safety, they are more concerned with changes in cell viability than methods such as lactate dehydrogenase cytotoxicity assays. According to different principles, cell viability detection methods are mainly divided into metabolic method, enzyme activity method and ATP method.
2.1 Metabolism
2.1.1 Principles and introduction
Metabolic method is the most common method for detecting cell proliferation, and mainly includes Tetrazolium reduction, such as MTT and CCK-8 methods, and Resazurin Reduction, such as alamarBlue method. The principles of these methods are based on the metabolic capacity of the cells to reduce the substrate of the incubation. The products usually have light absorption or fluorescence properties, so high-throughput cell viability analysis can be performed with a microplate reader.
Among the above methods, the most common one is the MTT method, which belongs to the microplate reader light absorption application, which utilizes the succinate dehydrogenase in the mitochondria to reduce the MTT, forms water-insoluble crystalline formazan (Formazan) and deposits on the cells. Neutralizes extracellular. Finally, it is dissolved at a specific wavelength of 570 nm using a specific organic solvent such as dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) [Fig. 1]. Since MTT itself has a positive charge, it easily enters cells and has certain metabolic toxicity. At the same time, exactly, the MTT method is to detect the metabolic activity of mitochondria in cells.
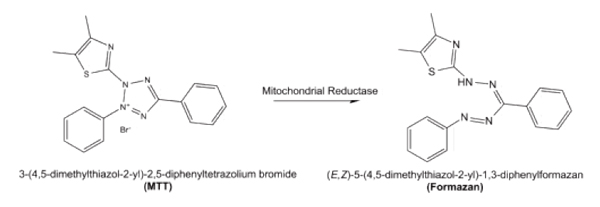
Figure 1, the principle of MTT, the picture is from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MTT_assay
In recent years, a series of similar structures on the basis of MTT have been applied to the detection of cell proliferation activity, mainly including MTS, XTT, and WST, which are also the application of the microplate reader. Unlike MTT, these substrates have a negative charge and are therefore not easily accessible to cells, and their reduction products are soluble in water, so there is no need to dissolve the crystallization step, which improves the operability and stability of the experiment. The most common in this series is the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8 method) based on WST-8. Compared with the MTT assay, which relies solely on mitochondrial dehydrogenase, the CCK-8 assay is based on the majority of dehydrogenases in the cell, so its detection activity is more accurate, more sensitive, and reduces cytotoxicity [Figure 2]. Since the dissolution step is omitted, the CCK-8 method supports kinetic detection, which increases the flexibility of the experiment. At the same time, because of its low toxicity, cells can be used for subsequent tests after completion of CCK-8 assay.
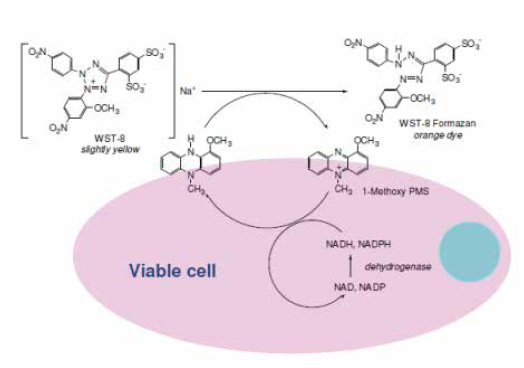
Figure 2, CCK-8 principle, picture from
The above-mentioned metabolic methods belong to the optical absorption application of the microplate reader. Although relatively economical, they are subject to various limitations of light absorption itself, especially the narrow dynamic range, and are easily interfered by reagents and drugs having light absorption characteristics. At the same time, the light absorption method is limited by the optical path factor in Beer's law, and is not suitable for higher-throughput detection such as 384 or 1536-well plates. Therefore, the fluorescence detection-based metabolic method has also become one of the main methods for detecting cell viability, and the common method is the alamarBlue method based on resazurin reduction.
In principle, the alamarBlue method is similar to the MTT and CCK-8 methods, and uses the inherent metabolic capacity of the proliferating cells to reduce the colorless, non-fluorescent resazurin. The resulting red product resorufin has strong fluorescent properties, so it can be used to support fluorescence or light. The absorption of the microplate reader is tested to improve the flexibility and anti-interference ability of the test [Figure 3]. The alamarBlue method, which supports fluorescence detection, can have 3-4 dynamic orders with a wider detection range and higher sensitivity. At the same time, the reduced product is soluble in water and low in toxicity, thus supporting kinetic detection and multiplex detection as well as CCK-8. However, the alamarBlue method is more stable and therefore very suitable for tracking cell proliferation changes.
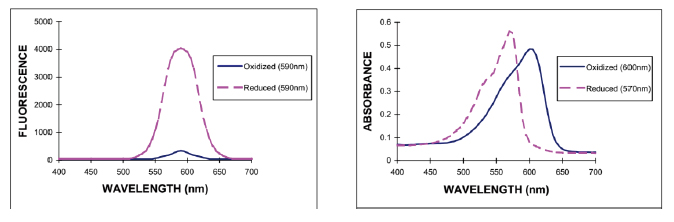
Figure 3. Fluorescence (left, 530-560 nm excitation) and light absorption (right) before and after the alamarBlue reaction. Image courtesy of Invitrogen Technical Materials
2.1.2 Support from Molecular Devices
For the metabolic method, MD mainly provides hardware and software support. Among them, single-function and multi-function microplate readers equipped with light absorption on hardware, such as cMAX plus, Spectra-Max M series, etc., support MTT method and CCK-8 method. High throughput testing. Correspondingly, microplate readers with fluorescence detection functions such as SpectraMax iD3/5, SpectraMax Gemini EM, SpectraMax i3X and M series are recommended for fluorescence cell viability assays. In software, on the one hand, Cell Growth & Viability in the Softmax Pro 7 template library has preset some common method templates, such as alamarBlue method and MTS method. A similar method only needs to change the detection parameters on the preset template, and the modified template can be saved as a new template for subsequent detection. On the other hand, the software supports multiple forms of data processing, including dual-wavelength correction, blank subtraction, data homogenization to late linear, four-parameter fitting, etc., which greatly facilitates the analysis process and improves analysis efficiency and consistency. .
2.1.3 Common experimental procedures and precautions
The experimental procedure of the metabolic method is basically the same. Taking the MTT method as an example [Fig. 5], it is mainly divided into the following steps.
a) Pre-plated cells in 96-well plates, cell density needs to be optimized according to the cell line itself and the experimental purpose (proliferation viability or drug toxicity screening). In general, the density of suspended cells is higher than that of adherent cells. The plate type glazing method recommends a transparent plate, and the fluorimetry method recommends a black edge bottom transparent plate.
b) Perform compound or similar treatment as required. The experiment in this step requires optimization of the initial treatment time and incubation time of the drug. It is important to note that the metabolic method requires the substrate to be added by cell metabolism. Therefore, it is necessary to maintain the cells for further staining in the proliferation stage. In this step, you also need to pay attention to the choice and settings of the control, including system control (only cells or only MTT dye plus drugs) and positive control (solvent treatment group in cytotoxic experiments, etc.).
c) Perform substrate incubation, which requires optimization of the time and concentration of substrate incubation. Pay attention to the fluorescence method and take care to avoid this step.
d) Dissolve the crystals from the reaction. This step needs to ensure complete dissolution of the crystals, while ensuring that the lysate does not affect the final detection. Usually the dissolution of acidification will avoid the effect of phenol red on the final detection. This step is not required for the CCK-8 method and the alamarBlue method.
e) Single-wavelength or dual-wavelength detection using a microplate reader. The general MTT method has a single wavelength of 570 nm and dual wavelengths of 570 nm-630~690 nm for correcting cell debris or turbidity interference [Fig. 5]. If it is a fluorescence method, fluorescence detection is performed according to the recommended parameters. The CCK-8 method and the alamarBlue method can perform kinetic tests as required. When performing kinetic testing, it is recommended that the microplate reader be preheated to 37 °C.
Processing and analysis results, correlated dual-wavelength correction, homogenization and linear/quadruple fitting can be done in the Softmax Pro software.
Substrates of the metabolic method are detected by a reduction reaction, and thus are affected by compounds and reagents having reducing ability. In addition, compounds having light absorbing properties and fluorescent properties may affect the light absorption methods such as the MTT method and the CCK-8 method and the fluorescence method such as the alamarBlue method. For the above effects, on the one hand, it can be excluded by direct mixing of compounds and substrates, and on the other hand, it can be further analyzed by other cell viability detection methods.
Click to download the full version of the application manual
2.2 Enzymatic method
2.2.1 Principles and introduction
2.2.2 Support from Molecular Devices
2.2.3 Common experimental procedures and precautions
2.3 ATP method
2.3.1 Principles and introduction
2.3.2 Support from Molecular Devices
2.3.3 Common experimental procedures and precautions
Third, cytotoxicity and killing analysis
Although the above cell viability assay method is widely used for toxicity analysis, its direct change from cell viability is not a direct analysis of cytotoxicity. At the same time, with the rise of the field of immunity, more and more studies have begun to pay attention to direct Cytotoxicity, especially the detection of cell lysis. In this chapter, we will introduce some common tests that are biased towards the toxicity of immune cell killing.
3.1 LDH cytotoxicity method
3.2 Calcein release method
3.3 Luciferase release method
Click to download the full version of the application manual
Click to download the full version of the application manual
We're professional uterine manipulator manufacturers and suppliers in China, specialized in providing high quality medical instruments with reasonable price. We warmly welcome you to buy or wholesale bulk uterine manipulator for sale here and get quotation from our factory.
Uterine Manipulator,Gynecology Uterine Manipulator,Uterine Manipulator Instrument,Laparoscopic Uterine Manipulator
Tonglu WANHE Medical Instrument Co., Ltd , https://www.tlvanhurhealth.com