[ China Pharmaceutical Network Technology News ] The efficiency of developing new drugs is very low. Of all the drugs that entered the clinical trial, less than 12% of the drugs at the end could appear in the pharmacy. It is mainly done by spraying the compounds and chemicals one by one into the culture dish of the diseased cells. Currently, more and more drug developers are turning to computers and artificial intelligence to reduce the list of potential drug molecules, saving test time and money.
It is understood that the AI ​​algorithm can recognize genes encoding proteins with good drug binding potential. Now a new paradigm in science and translational medicine – adding new levels of complexity to shrink on-site binding proteins, drugs and clinical data to better predict which genes are most likely to enable drugs to bind proteins.
Blind development may be one of the important reasons for drug development failure. Genetic epidemiologist Aroon Hingorani said, "Many causes can lead to drug development failure." “The main reason is that there is no correct goal for the disease.†A drug may show initial prospects in early experiments with cells, tissues, and animal models, but these drugs are often too simplistic and rarely subject to randomization and blinding. test. For example, the most common pattern of schizophrenia is the onset of a sudden jump, a behavior known as "burst" - not the most natural model of human response to psychotropic drugs. Scientists use these results to estimate which proteins are targeted, but because these studies tend to be small and short, there are many ways to interpret the results.
When you are developing drugs, time is money. When effectively saving development time, it is actually reducing the cost of capital investment. Researchers estimate that about 15% to 20% of new drug costs are entering the discovery phase. Typically, this represents hundreds of millions of dollars in investment and 3 to 6 years of work. The calculations promise to shorten the process to a few months at a price of tens of thousands of dollars. However, there are currently no drugs on the market that have been selected by an AI system, but they are in a state of preparation.
Hororani's team established a predictive model that combines genetic information with protein structure data and known drug interactions. They have access to nearly 4,500 potential drug targets, doubling the previous estimate of the number of human genomes as “medicinalâ€. Then, two clinicians combed the 144 drugs of the correct shape and chemical substance with their established protein binding targets. These have passed safety tests, which means they can be quickly re-used for other diseases.
More and more companies are looking for new ways to develop drugs and improve development efficiency. One of Hororani's collaborators is BenevolentAI, vice president of biomedical informatics at AI in the UK. The company recently signed an agreement to acquire and develop clinical phase drug candidates for Janssen (Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceuticals). They plan to start Phase IIb trials later this year. Last month, Japanese ophthalmology giant Sanden signed an agreement with Palo Alto's two-eye hospital to use AI-driven technology to identify glaucoma candidates. A few weeks ago, two European companies, Pharnext and Galapagos, collaborated to use computer models to find new treatments for neurodegenerative diseases.
Long-term drug pipeline researcher Derek Lowe wrote a blog about science subjects, and he said he is often skeptical about purely computational methods. "In the long run, I didn't see this thing is impossible," he said. "But if someone comes to me, they can only predict the activity of the entire compound list. For example, I might think it is nonsense. I want to see a lot of evidence before I believe.
Companies like TwoXAR are working hard to build such evidence. Last fall, they collaborated with Stanford University's Asian Liver Center to screen 25,000 potential adult liver cancer candidates. Working at an abandoned nail salon in Palo Alto, they screened out computer software through genetics, proteomics, drugs and clinical databases to identify 10 possible treatments. Samuel Sue, director of the Liver Center, was surprised by the list they brought back: it included several predictions made by laboratory researchers. So he decided to test the most promising of all, killing five different liver cancer cells without harming healthy cells, and is now conducting human trials.
The only existing FDA-approved treatment for cancer takes five years to develop. What's exciting is that for industries with such high failure rates, even a small increase in success rate could be a multi-billion dollar gain. The application of artificial intelligence technology will play a huge role in drug development.

(Supercomputer helps new drug development to display great value. Image Source: Baidu Pictures)
It is understood that the AI ​​algorithm can recognize genes encoding proteins with good drug binding potential. Now a new paradigm in science and translational medicine – adding new levels of complexity to shrink on-site binding proteins, drugs and clinical data to better predict which genes are most likely to enable drugs to bind proteins.
Blind development may be one of the important reasons for drug development failure. Genetic epidemiologist Aroon Hingorani said, "Many causes can lead to drug development failure." “The main reason is that there is no correct goal for the disease.†A drug may show initial prospects in early experiments with cells, tissues, and animal models, but these drugs are often too simplistic and rarely subject to randomization and blinding. test. For example, the most common pattern of schizophrenia is the onset of a sudden jump, a behavior known as "burst" - not the most natural model of human response to psychotropic drugs. Scientists use these results to estimate which proteins are targeted, but because these studies tend to be small and short, there are many ways to interpret the results.
When you are developing drugs, time is money. When effectively saving development time, it is actually reducing the cost of capital investment. Researchers estimate that about 15% to 20% of new drug costs are entering the discovery phase. Typically, this represents hundreds of millions of dollars in investment and 3 to 6 years of work. The calculations promise to shorten the process to a few months at a price of tens of thousands of dollars. However, there are currently no drugs on the market that have been selected by an AI system, but they are in a state of preparation.
Hororani's team established a predictive model that combines genetic information with protein structure data and known drug interactions. They have access to nearly 4,500 potential drug targets, doubling the previous estimate of the number of human genomes as “medicinalâ€. Then, two clinicians combed the 144 drugs of the correct shape and chemical substance with their established protein binding targets. These have passed safety tests, which means they can be quickly re-used for other diseases.
More and more companies are looking for new ways to develop drugs and improve development efficiency. One of Hororani's collaborators is BenevolentAI, vice president of biomedical informatics at AI in the UK. The company recently signed an agreement to acquire and develop clinical phase drug candidates for Janssen (Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceuticals). They plan to start Phase IIb trials later this year. Last month, Japanese ophthalmology giant Sanden signed an agreement with Palo Alto's two-eye hospital to use AI-driven technology to identify glaucoma candidates. A few weeks ago, two European companies, Pharnext and Galapagos, collaborated to use computer models to find new treatments for neurodegenerative diseases.
Long-term drug pipeline researcher Derek Lowe wrote a blog about science subjects, and he said he is often skeptical about purely computational methods. "In the long run, I didn't see this thing is impossible," he said. "But if someone comes to me, they can only predict the activity of the entire compound list. For example, I might think it is nonsense. I want to see a lot of evidence before I believe.
Companies like TwoXAR are working hard to build such evidence. Last fall, they collaborated with Stanford University's Asian Liver Center to screen 25,000 potential adult liver cancer candidates. Working at an abandoned nail salon in Palo Alto, they screened out computer software through genetics, proteomics, drugs and clinical databases to identify 10 possible treatments. Samuel Sue, director of the Liver Center, was surprised by the list they brought back: it included several predictions made by laboratory researchers. So he decided to test the most promising of all, killing five different liver cancer cells without harming healthy cells, and is now conducting human trials.
The only existing FDA-approved treatment for cancer takes five years to develop. What's exciting is that for industries with such high failure rates, even a small increase in success rate could be a multi-billion dollar gain. The application of artificial intelligence technology will play a huge role in drug development.
Boob tape, breast lift tape
Boob tape is based on 95% cotton and 5% Elastic Spandex fabric. The material is safe, soft, breathable, which makes you comfortable in it. It has super strong elasticity, lateral stretching is more than 230%. It is coated with imported wave pattern glue, which ensures the tape has stable adhesion and easy to remove, do not hurt your skin. It has a certain waterproof effect, the adhesion will not be reduced even you are sweaty or swimming. It has wonderful lifting and gathering effect, let you have a proud chest curve.
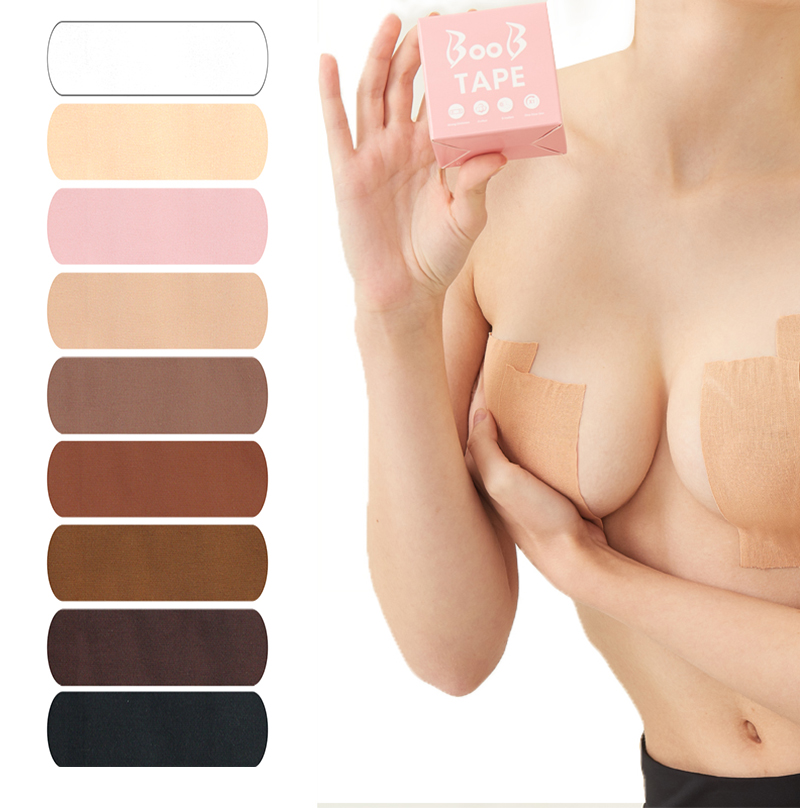

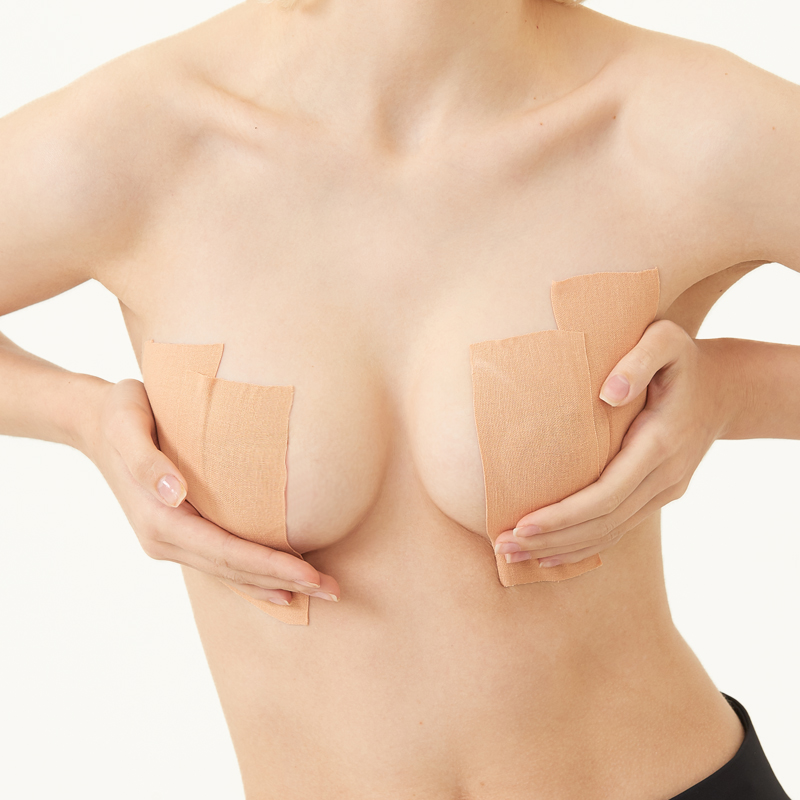
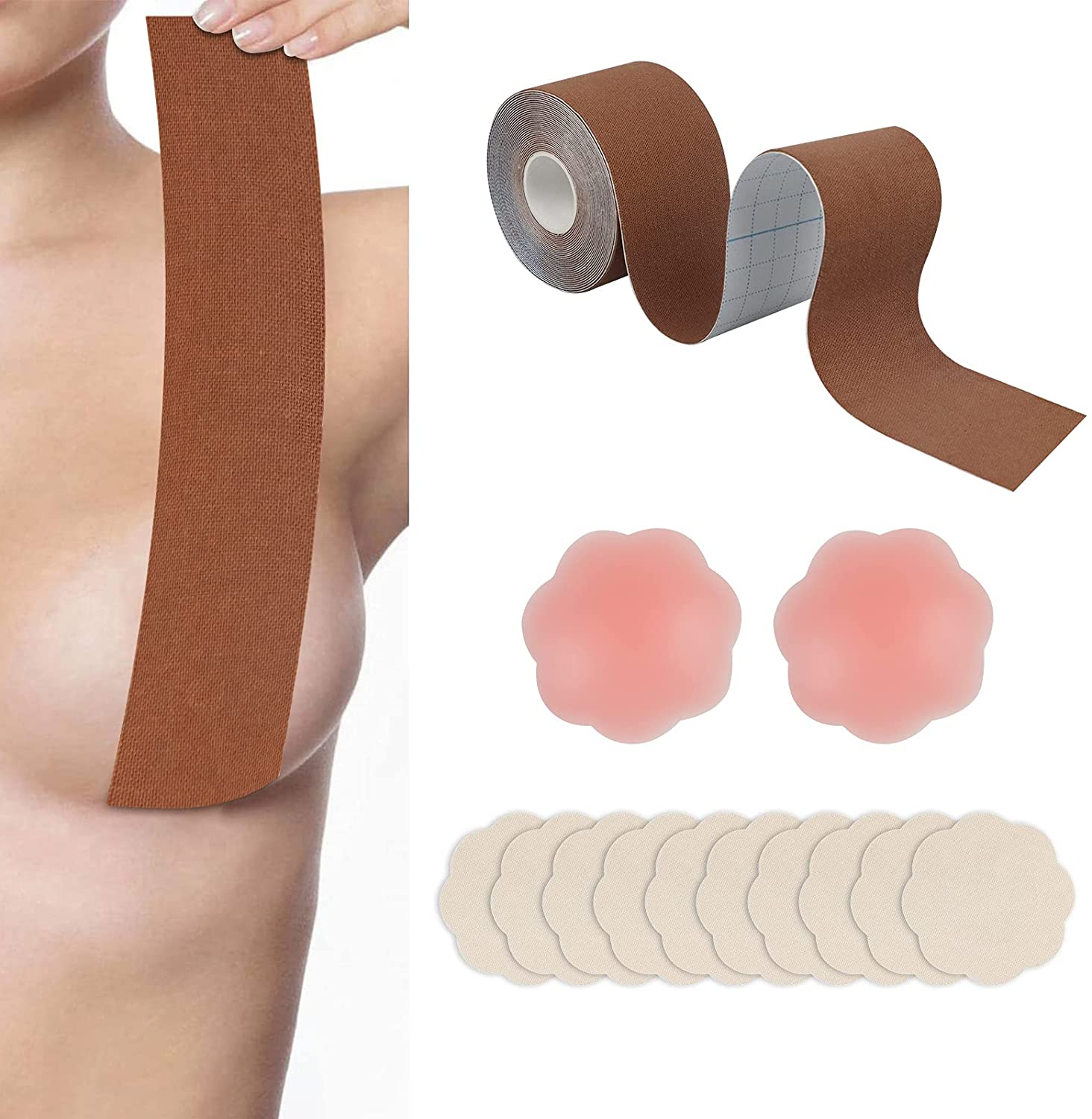
boob tape,breast lift tape,boob tape and nipple cover,boob lift tape,breast tape
Kunshan Jieyudeng Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.jerrytapes.com