It is understood that there are four problems that cannot be ignored in the current summer corn production, which are the limiting factors for the high yield and high yield of summer corn. The relevant circumstances are described as follows:
The seed selection is not careful: Because the current seed-bridging system is not yet perfect, unqualified corn seed still occupies a large proportion. Some peasants are guilty of "cheating on cheapness." They have been buying small quantities of so-called fine varieties at low prices from small traders or informal seed management departments, leading to serious reductions in production. Most of these seeds are private individuals, and the seed production procedures are unscientific and their purity is not up to standard.
Suggestions: We hope farmers' friends can overcome the "fight for cheap" mentality and go to a seed company with good reputation or a formal seed production unit to purchase genuine breeds suitable for cultivation in the region. In order to save a few yuan of seed money, it is not worthwhile to reduce production.
Density is unreasonable: Too much planting density is the most outstanding problem in the current summer corn production. For example, some farmers planted more than 5,000 planted acres of “Nongda 108â€, about 1/3 more than the suitable density of the plant. . Due to the high density, the single plant has poor growth and development, high empty culm rate, and severe baldness of the ear, resulting in different degrees of lodging, resulting in reduced yields.
Recommendation: Proper close planting is an important part of achieving high yield in summer corn. Each species has its own suitable density range, such as a longer growth period, big spike type "Nongda 108", spring sowing density 3000-3500 strains / acre, summer sowing density 3500-4000 strains; Jingyu 7 general density 3700 - 4000 plants/mu is appropriate, high-fertilizer land mass no more than 4500/mu; Jingyu No. 11 general density 3800–4100 plant/mu; Mindan 22 optimum density 3500-4000 plant/mu; high-yield large panicle strains The planting density of Liaodan 127 in the East and North China areas with slightly flat development is 2800-3000 plants/mu, and Zhongdan 808 with high light efficiency and big panicle and large grain varieties is suitable for about 2800 plants per mu.
In addition, the density of the same species also depends on the fertility and sowing date; the soil fertility should be high density, the middle and lower fertility plots should be thin; early sowing should be diluted, and late sowing should be dense.
Fertilization is unscientific: In the fertilization, there is a common phenomenon of diazo fertilizer, light phosphorus fertilizer, neglect of potassium fertilizer and trace fertilizer. Because the crop yield is restricted by the minimum nutrient law, a single excessive fertilization cannot achieve high yields. Instead, due to too much nitrogen fertilizer application, poor lodging resistance and serious diseases and insect pests may occur, resulting in different degrees of reduction in production. In addition, improper fertilization and blind application of certain effective nutrient contents (Note: the pure content of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, and the medium and trace elements should not be counted) are too low for “maize specific fertilizersâ€. Caused a drop in production.
Suggestion: Phosphorus, Potassium Fertilizer and Trace Fertilizer should be used for deep seeding at the time of sowing, or before the jointing stage. (Note: For formerly glutinous wheat, fertilize all-round and more plots, it can be applied less or not.) Nitrogen fertilizers should be applied in phases, with 2/3 and 1/3 of the total nitrogen fertilization applied at the jointing stage and the big bell stage, respectively. The same amount of fertilization can be used to increase the production rate of the "one-shot shelling" fertilization in the big bell-mouth stage. .3%-22%. Combining spraying with foliar fertilizer during the growth period can significantly increase yield.
The idea that watering is not timely depends on days and rain is serious. It is not always based on the water requirement of corn that it is poured into “critical waterâ€. Instead, it is poured into water to “save life†when it is affected by drought, which seriously affects the yield. When the plants showed symptoms of drought, they were already severely dehydrated.
Suggestion: Under the premise of planting the athlete's foot, when the drought occurs during the growth period, it is necessary to pour in jointing and booting water, heading flowering water, and grouting water in time to meet the high-yielding water requirement of the summer corn.
The seed selection is not careful: Because the current seed-bridging system is not yet perfect, unqualified corn seed still occupies a large proportion. Some peasants are guilty of "cheating on cheapness." They have been buying small quantities of so-called fine varieties at low prices from small traders or informal seed management departments, leading to serious reductions in production. Most of these seeds are private individuals, and the seed production procedures are unscientific and their purity is not up to standard.
Suggestions: We hope farmers' friends can overcome the "fight for cheap" mentality and go to a seed company with good reputation or a formal seed production unit to purchase genuine breeds suitable for cultivation in the region. In order to save a few yuan of seed money, it is not worthwhile to reduce production.
Density is unreasonable: Too much planting density is the most outstanding problem in the current summer corn production. For example, some farmers planted more than 5,000 planted acres of “Nongda 108â€, about 1/3 more than the suitable density of the plant. . Due to the high density, the single plant has poor growth and development, high empty culm rate, and severe baldness of the ear, resulting in different degrees of lodging, resulting in reduced yields.
Recommendation: Proper close planting is an important part of achieving high yield in summer corn. Each species has its own suitable density range, such as a longer growth period, big spike type "Nongda 108", spring sowing density 3000-3500 strains / acre, summer sowing density 3500-4000 strains; Jingyu 7 general density 3700 - 4000 plants/mu is appropriate, high-fertilizer land mass no more than 4500/mu; Jingyu No. 11 general density 3800–4100 plant/mu; Mindan 22 optimum density 3500-4000 plant/mu; high-yield large panicle strains The planting density of Liaodan 127 in the East and North China areas with slightly flat development is 2800-3000 plants/mu, and Zhongdan 808 with high light efficiency and big panicle and large grain varieties is suitable for about 2800 plants per mu.
In addition, the density of the same species also depends on the fertility and sowing date; the soil fertility should be high density, the middle and lower fertility plots should be thin; early sowing should be diluted, and late sowing should be dense.
Fertilization is unscientific: In the fertilization, there is a common phenomenon of diazo fertilizer, light phosphorus fertilizer, neglect of potassium fertilizer and trace fertilizer. Because the crop yield is restricted by the minimum nutrient law, a single excessive fertilization cannot achieve high yields. Instead, due to too much nitrogen fertilizer application, poor lodging resistance and serious diseases and insect pests may occur, resulting in different degrees of reduction in production. In addition, improper fertilization and blind application of certain effective nutrient contents (Note: the pure content of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, and the medium and trace elements should not be counted) are too low for “maize specific fertilizersâ€. Caused a drop in production.
Suggestion: Phosphorus, Potassium Fertilizer and Trace Fertilizer should be used for deep seeding at the time of sowing, or before the jointing stage. (Note: For formerly glutinous wheat, fertilize all-round and more plots, it can be applied less or not.) Nitrogen fertilizers should be applied in phases, with 2/3 and 1/3 of the total nitrogen fertilization applied at the jointing stage and the big bell stage, respectively. The same amount of fertilization can be used to increase the production rate of the "one-shot shelling" fertilization in the big bell-mouth stage. .3%-22%. Combining spraying with foliar fertilizer during the growth period can significantly increase yield.
The idea that watering is not timely depends on days and rain is serious. It is not always based on the water requirement of corn that it is poured into “critical waterâ€. Instead, it is poured into water to “save life†when it is affected by drought, which seriously affects the yield. When the plants showed symptoms of drought, they were already severely dehydrated.
Suggestion: Under the premise of planting the athlete's foot, when the drought occurs during the growth period, it is necessary to pour in jointing and booting water, heading flowering water, and grouting water in time to meet the high-yielding water requirement of the summer corn.
Rabies Vaccine (Vero Cell) for Human Use
The first company develops and employs the technology of microcarrier bioreactor for production of Rabies Vaccine (Vero Cell) for Human Use in China. The culturing process has good repeatability, the product shows reliable quality and in reasonable stability and has the comparable effect with lyophilized formulation.
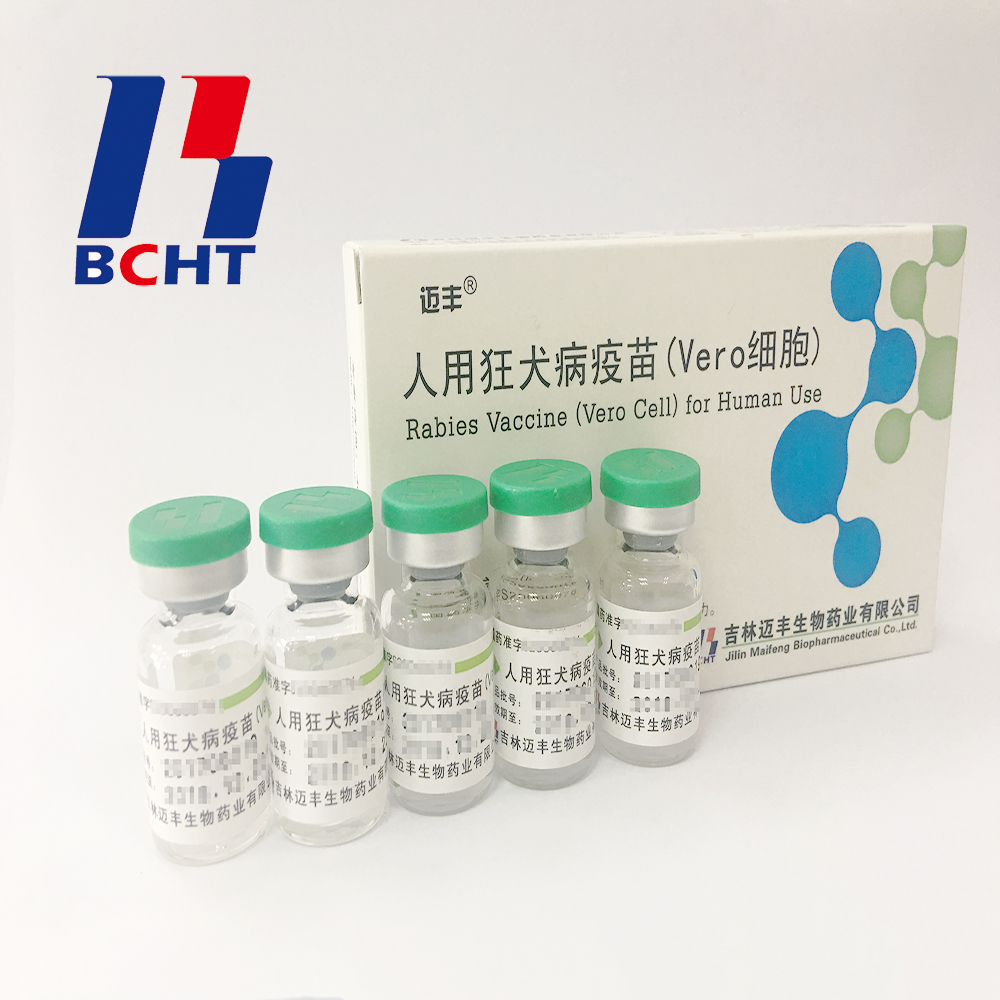
Rabies Vaccine,Freeze-Dried Rabies Vaccine,Mild Rabies Vaccine,Stable Rabies Vaccine For Human Use
Changchun BCHT Biotechnology Co. , http://www.ccbcht.com