
Introduction
Engineered nanoparticles (ENP) through wastewater discharge may contain errors ENP product disposal, as well as outdoor applications such as leaching way into natural water bodies, resulting in potential contamination of the environment, which led to widespread concern 1-3. If mixed into drinking water sources ENP, need assessment off
Key to the fate of ENP during drinking water treatment . Flocculation precipitation is one of the primary treatment to remove all kinds of particles from drinking water. Therefore, we need to understand standard coagulation process ENP behavior in order to accurately predict the human condition through contact with drinking water ENP 4. Single-particle ICP-MS ( SP-ICP-MS ) technology is an important advancement in the field of ENP environmental monitoring, enabling rapid assessment of ENP size, quantity and dissolved metal concentration by simple pretreatment . The newly developed SP-ICP-MS method is suitable for the characterization and quantification of silver, gold, titanium dioxide, zinc oxide and cerium oxide ENP in water 5,6 .
Due to the large amount of ENP used in consumer goods and commodities , this work focuses on five common ENPs : silver, gold, titanium dioxide, zinc oxide and cerium oxide. The behavior of these particles during flocculation was evaluated by SP-ICP-MS in two types of surface water . For more details, see the recent development in the journal "Chemosphere" paper 7. These experiments used a 4- zone floc, also known as floc removal. When the flocculant is added until the point of dissolution, floc removal occurs, causing the insoluble "flocs" to clump together. Other particles will be condensate water into flocs, and is cleared in the settling process. Due to its ease of use, this technology is the most commonly used flocculation method in wastewater and drinking water treatment systems .
experiment
material
Citrate stabilized silver nanoparticles (40, 70, and 100 nm diameter) and the gold particles (50, 80, and 100 nm diameter) 2 mM sodium citrate were purchased from nanoComposix, Inc.. ( San Diego, California , USA). Non-coated titanium dioxide (100 nm), ceria (30-50 nm), and zinc oxide (80-200 nm) nanoparticles are purchased from US Research Nanomaterials, Inc.. (Houston, Texas). A stock suspension of ENP was prepared in deionized water . Prepared by dissolving in water a silver matrix type, the gold, titanium, cerium and zinc standard solution, to achieve a minimum of matrix effects, for instrument calibration purposes.
In order to simulate the flocculation process, aluminum sulfate ( Al 2 (SO 4 ) 3 ∙ 18H 2 O ), ferric chloride ( FeCl 3 ∙ 6H 2 O ) and iron sulfate ( Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 ∙ 4H 2 O ), etc. the most commonly used coagulant are purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientic, Inc.. (USA Pennsylvania Pittsburgh). River water samples were taken from the Missouri River, and water samples were taken from the city of Rolla, Missouri Schumann Lake. Feet from the water at about two miles from the river bank below the sample collection. Pre-cleaned using a polypropylene bottle samples collected, and after being stored at a refrigerator until use. The refrigerated samples were placed in a room temperature environment prior to use .
Instrument and SP-ICP-MS method
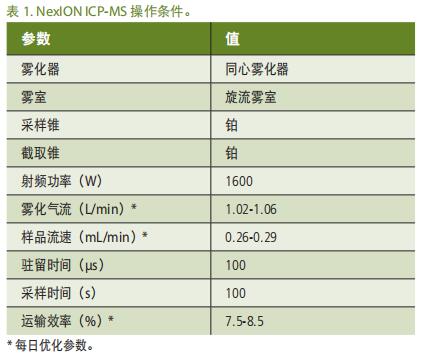
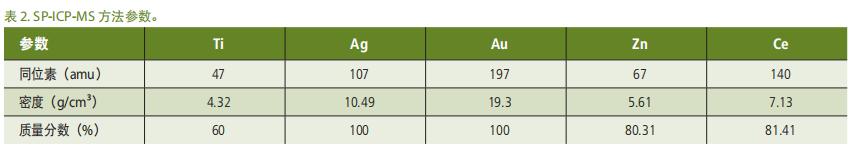
Sample analysis and data processing were performed using a PerkinElmer NexION® ICP-MS equipped with a SyngistixTM nanoapplication software module . Instrument and method parameters are shown in Tables 1 and 2 , see References 8, 9 for more details . To avoid interference from 48 Ca to 48 Ti , select 47 Ti for analysis.
Flocculation
Flocculation process (Phipps and Bird) was stirred using a hexagonal-shaped head and a square 2 L beaker. After adding 2 L of water to the beaker, 70 nm gold ( 5 μg/L gold), 80 nm silver ( 2 μg/L silver), 100 nm titanium dioxide ( 6 μg/L titanium), 30-50 nm dioxide were sequentially oxidized. cerium (5 μg / L of cerium) zinc oxide and 80-200 nm (6 μ g / L Zn) was added into the beaker and the like nanoparticles, and stirring rate at 100 rpm for 1 minute nanoparticle dispersion. The known concentration of flocculation agent is added to the beaker and stirring speed at 300 rpm for 30 seconds (fast mix), and respectively 58, 42 and 28 rpm stirring speed for 10 minutes (flocculation stage), and finally still precipitate for 3 hours. Sampling immediately after dispersion and precipitation, to assess changes after the particle size of the treated nanoparticles, and the concentration of dissolved ion concentration.
This study focused on a specific type of flocculation treatment: Zone 4 flocculation, by adding a certain amount of flocculant, to form an insoluble precipitate. The particles accumulate in the precipitate and are then removed by settling.
For details, click the button below to request information.
Organic Rhodiola Rosea Extract
Organic Rhodiola Rosea extract is an extract from the root of Rhodiola Rosea. Organic Rhodiola Rosea Extract is a herb extract. It has a sweet smell and a bitter taste. The main ingredients are salidroside, aglycone tyrosol, and rosavin, which have the effects of enhancing immune function, protecting cardiovascular and cerebrovascular, anti-cancer, and anti-depressive effects.
As a professional manufacturer and supplier of Organic Rhodiola Rosea extract, our Rhodiola Rosea extract is produced, processed, and stored in strict accordance with EU and USDA organic standards. Our Organic Rhodiola Rosea extract is 100% traceable.
Our Rhodiola Rosea extracts are all extracted from wild-collected Rhodiola roots. Afterward, it is processed and stored in an organic environment. All these processes are fully traceable and verifiable.
Rhodiola Rosea Extract,Organic Rhodiola Rosea Extract,Rhodiola Rosea,Organic Rhodiola Rosea
Organicway (xi'an) Food Ingredients Inc. , https://www.organicwayince.com


