The latest issue of the New England Journal of Medicine published a clinical study of two Down's screenings for pregnant women aged 10-14 weeks of pregnancy, 1 to compare traditional combined screening methods for early pregnancy screening in pregnant women ( Clinical manifestations of fetal free DNA (cfDNA) detection in maternal peripheral blood in NT screening of the posterior neck of the fetus + screening of serum student indicators.
The study recruited 18,955 pregnant women over the age of 18 and 10-14 weeks of gestation through 35 international centers in six countries, blood-sucking and simultaneous early pregnancy screening and Roche Harmony Down's screening test. And only the results of joint screening for pregnant women. The results of the joint screening and Harmony Down's screening were finally verified by genetic diagnostic techniques and examinations of the born babies. The clinical research process is shown in Figure 1:
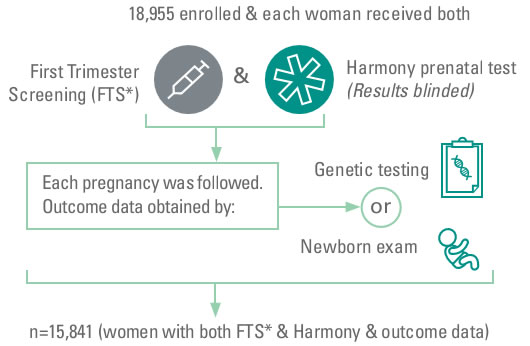
Figure 1 Flow of Harmony compared to joint screening technology
In the results of the first phase of the study, the researchers compared the results of two technical routes to the 21-trisomy (Down's syndrome). For 15841 pregnant women and fetuses with both combined screening and Harmony test results, Harmony's detection rate for 21-trisomy was 100% (38/38), and combined screening for 21-trisomy detection rate 78.9% (30/38); Harmony's false positive rate for the 21-trisomy test was 0.06% (9/15841), and the false positive rate for the 21-trisomy test was 5.4% (854/15841). Harmony's positive predictive value for the 21-trisomy test was 80.9% (38/47), and the combined predictive value for the 21-trisomy test was 3.4% (30/884). Thus, cfDNA-based Harmony detection provides higher sensitivity, lower false positive rates, and higher positive predictive values ​​than traditional joint screening. The results of the clinical study are shown in Figure 2:
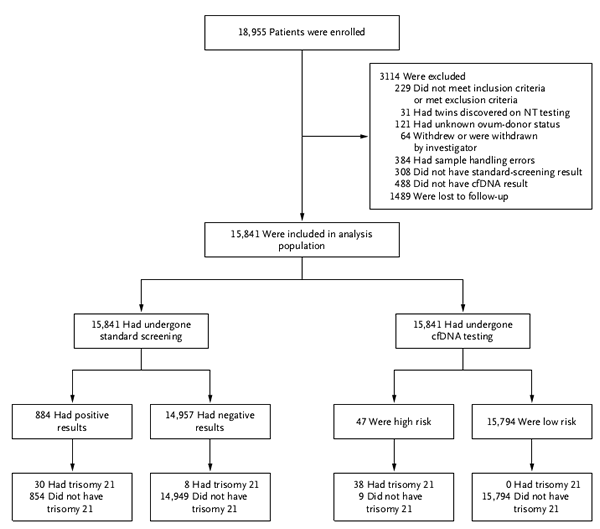
Figure 2 Comparison of test results of 18955 pregnant women receiving two Down's screening techniques
In the results of the second phase of the study, the authors further compared the results of the two technical routes to the 18-trisomy and 13-trisomy. As shown in Figure 3, the cfDNA-based Harmony assay also has higher sensitivity to 18-trisomy and 13-trisomy, a higher positive detection rate and a lower false positive rate.
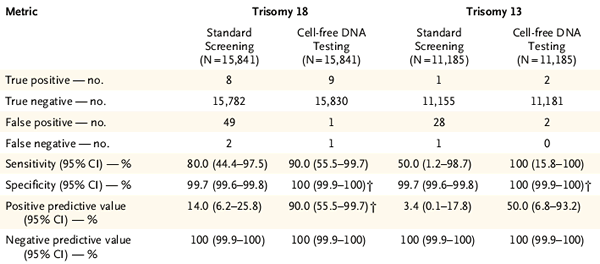
Figure 3 Combined screening and Harmony's comparison of 18-trisomy and 13-trisomy
It is noteworthy that cfDNA-based Down's screening technology has always been applied to high-risk pregnant women (age older than 35 years) as a technical advantage, because its low false positive rate can reduce the probability of high-risk pregnant women receiving invasive diagnosis, reducing unnecessary risks of. As technology matures, most cfDNA-based assays are available for low-risk pregnant women. Roche Harmony's non-invasive Down's screening technique also confirmed its feasibility for pregnant women of 18-50 years of age in previous clinical studies 2 . In this study, the authors also analyzed the clinical presentation of Harmony's 21-trisomy test for high-risk and low-risk pregnant women. As shown in Figure 4, Harmony's detection sensitivity and positive detection rate for high-risk and low-risk pregnant women are also higher than combined screening.
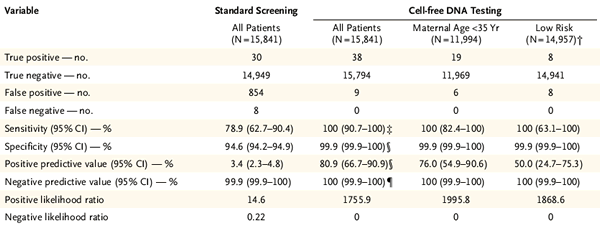
Figure 4 Harmony test results for high-risk and low-risk pregnant women
Recently, the clinical application of NIPT has received wide attention. Many companies are trying to expand the content of non-invasive prenatal screening to detect the risk of diseases such as rare chromosomal abnormalities in low-risk pregnant women, resulting in an increase in overall positive results. Significantly increase the risk of pregnant women erroneously terminating pregnancy.
In the same period of the New England Journal of Medicine, an article "Accurate Description of DNA-Based Noninvasive Prenatal Screening" randomly selected and evaluated the positive detection results obtained by 307 non-invasive prenatal companies in the market. Among these positive results, the researchers found that some physiological factors may lead to non-invasive prenatal screening false positive results, such as copy number variation, placental mosaic, maternal somatic mosaic. Compared with more than 22,000 clinical research samples before Roche Ariosa, due to the small sample size of this study, it is impossible to strictly compare these factors with the false positive results, so it is impossible to make any comparison of statistics such as false positive rate. . Researchers from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Gynaecology and Maternal Fetus Medical Association have suggested that after a positive result of non-invasive prenatal testing, it is necessary to confirm with interventional diagnosis before giving clear clinical guidance.
Roche Diagnostics is the world leader in in vitro diagnostics. Its Harmony non-invasive prenatal testing products have been supported by dozens of clinical studies, some of which have been published in high-quality medical journals, and currently more than 400,000 pregnant women in 100 countries worldwide. Enjoy the service . Roche Diagnostics will continue to provide safe and reliable services to customers and patients , and contribute to improving people's quality of life and reducing social medical costs.
All chart data in this article are from Roche Ariosa headquarters
1. Cell-free DNA Analysis for Noninvasive Examination of Trisomy. Norton et al, N Engl J Med. 2015
2. Noninvasive prenatal testing for fetal trisomies in a routinely screened first-trimester population. Nicolaides et al, AJOG 2012
Buckwheat Flours,Roasted Buckwheat Powder,Tartary Buckwheat Flour,Roasted Buckwheat
Huantai Biotechnology Co., Ltd. , https://www.huantaifds.com