Accurate counting and activity analysis of PBMC cells
First, the status of PBMC cell counting
1. At present, the vast majority of researchers are still using the blood cell counting board to manually count PBMCs under the microscope;
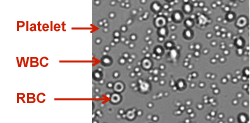
2. But under the microscope, because white blood cells and red blood cells are very close in size, they cannot completely distinguish between white blood cells and red blood cells;
3. Identification of red blood cells by the double concave shape of red blood cells requires an experienced operator and constantly adjusts the focus to identify; it is conceivable to identify each red blood cell, how long it takes, how strong it is needed The amount of work.
The difference in PBMC samples is large
Due to differences in individual differences (such as normal people and patients) and artificial separation, the degree of red blood cell and platelet contamination varies greatly, so we often see that the isolated PBMC samples vary widely (see the figure below), which is greatly increased. Under the same conditions, the difficulty of simply and accurately counting PBMC and the difficulty of detecting PBMC activity.
Second, the importance of accurate counting or vitality analysis of PBMC
PBMC (peripheral blood mononuclear cells) is the most commonly used cell model for immunological function studies, such as cell proliferation, cytotoxicity, and cytokine secretion.
For example, in the field of cancer immunotherapy, PBMC needs to be isolated from the patient's whole blood, and the isolated PBMC are further expanded or subjected to different functional tests. The activated cells are activated and returned to the patient for cell therapy. Cell concentration and cell viability are parameters that must be monitored throughout the process, from separation to detection, to culture, to reinfusion.
Density gradient separation fluid is the most commonly used method for isolating mononuclear cells from peripheral blood, bone marrow, and cord blood. However, inevitably, in the separated cells, residual red blood cells and platelets are mixed in mononuclear cells. The number of remaining red blood cells and platelets is related to the difference between individuals and the effect of separation; however, regardless of the high level of separation technology and the rich experience, there will inevitably be red blood cell and platelet contamination.
Characteristics of PBMC experiments
1. As time goes by, the cell quality declines;
2. The amount of samples related to clinical trials is large;
3. Cell samples are impure, the path of separation depends on patient samples and operators
How to accurately, quickly and easily count PBMC and accurately analyze PBMC activity is a crucial step in immunology research and immunotherapy.
1. Manually counting PBMC under the microscope using a hemocytometer, which is time consuming and labor intensive, and can not achieve accurate counting.
2. It is also impossible to distinguish red blood cells by the conventional cytometer of the bright field, and the purpose of accurately counting PBMC and accurate vitality analysis cannot be achieved.
3. There is an urgent need to replace manual counting with tools that quickly, easily, and accurately count PBMC. Nexcelom is in a market-leading position. Based on the conventional brightfield cell counter, a dual fluorescent cell viability analyzer has been developed for rapid and accurate counting and viability analysis of PBMC by AOPI dye.
references
1. Preliminary Report: Evaluation of Storage Conditions and Cryococktails during Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell Cryopreservation", LM Cosentino, W. Corwin, JM Baust, N.Diaz-Mayoral, H.Cooley, W. Shao, R. Van Buskirk, and JG Baust, Cell Preservation Technology, Volume 5 Number 4, 2007
2. "Viability and Functional Activity of Cryopreserved Mononuclear Cells", A. Weinberg, L. Zhang, D. Brown, A. Brice, B. Polsky, MS Hirsch, S. Owens, and K. Lamb Clincal and Diagnostic Laboratory Immunology, July, 2000, P714-716
3. "Cell loss and recovery in umbilical cord blood processing: a comparison of postthaw and postwash samples", V. Laroche, DH McKenna, G. Moroff, T. Schierman, D. Kadidlo, and J. McCullough, Transfusion, Vol. , 45, Dec. 2005.
4. "Viability and Recovery of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Cryopreserved for up to 12 Years in a Multicenter Study", CA Kleeberger, RH Lyles, JB Margolick, CR Rinaldo, JP Phair, and JV Giorgi, Clinccal and Diagnostic Laboratory Immunology, Vol. 6, No. 1, Jan. 1999.
Third, how to accurately count PBMC and vitality analysis
Dual fluorescence counting and viability analysis by AOPI dyes is an accurate counting method that can exclude red blood cells, platelets, cell debris and the like.
AO (acridine orange) and PI (propidium iodide) are nuclear staining reagents that can stain DNA. Among them, AO can embed the cell nucleus of all cells (live cells and dead cells) through the intact cell membrane, showing green fluorescence; PI can only embed the nucleus of all dead cells through the incomplete cell membrane, that is, the cell membrane of dead cells, showing red fluorescence.
Living dead mononuclear cells can exhibit a fluorescent signal. Mature red blood cells and platelets, because they have no nuclei, cannot be stained by AO/PI, so they can be completely excluded and not counted.
Double fluorescence counting and viability analysis by AOPI dye can accurately count the isolated PBMC and viability analysis, and can also perform PBMC in whole blood.
Example of sample PBMC count & activity analysis after separation        PBMC counting cells and activity analysis examples of whole blood samples
Bright field image shows RBC/ platelet contamination                        Brightfield images cannot be counted at all
        Dual fluorescence activity analyzer results report output                       Dual fluorescence activity analyzer results report output
Fourth, Cellometer cell counting and viability analysis instrument model selection
1. Dual fluorescence counting and viability analysis are the best choice for PBMC counting.
Three instrument models are available: AUTO2000/K2/ VISION CBA for accurate, fast and easy PBMC counting and vitality analysis.
AUTO2000 Dual Fluorescent Cell Viability Analyzer K2 Dual Fluorescence Cell Analyzer VISION CBA Cell Function Analysis System
Touch screen control Computer control Computer control, high configuration, analysis of apoptosis & cell cycle
2. The PBMC count is performed on the open cell automatic cell counter, and the PBMC viability test can be performed by the trypan blue exclusion method.
Although it can achieve automatic and rapid purposes, it can not effectively eliminate the interference of red blood cells and achieve accurate counting.
The trypan blue exclusion method detects cell death and death by adopting trypan blue, a cell-active dye that cannot pass through the normal and intact cell membrane of living cells, so living cells are not colored, but the cell membrane permeability of dead cells is increased, and the dye can pass through the cell membrane. Enter the cells and make the dead cells stain blue. It is the most commonly used method for detecting cell viability.
However, the trypan blue exclusion method cannot accurately count living cells because the cell membrane permeability is different, and the dye entering the cells is also very different, so it is often difficult to determine whether it is a dead cell or a living cell.
If the accuracy requirements for PBMC counting are not very high, but fast, automatic counting is required, and the consistency and repeatability of the experiment are high, the following three counters can be selected: AUTO1000/MINI/AUTO T4.
MINI automatic cell counter AUTO1000 integrated cell counter AUTO T4 automatic cell counter
Computer control, small and beautiful, cost-effective Integrated design, touch screen control Classic, in line with GLP / GMP
references
1. Chan, LL, Wilkinson, AR, Paradis, BD and Lai, N. (2012b) Rapid Image-based Cytometry for Comparison of Fluorescent Viability Staining Methods. Journal of Fluorescence 22, 1301-1311.
2. Almeida, C.-AM, Roberts, SG, Laird, R., McKinnon, E., Ahmed, I., Pfafferott, K., Turley, J., Keane, NM, Lucas, A., Rushton, B Chopra, A., Mallal, S. and John, M. (2009) Automation of the ELISpot assay for high-throughput detection of antigen-specific T-cell responses. Journal of Immunological Methods 344, 1-5.
3. Constantino, BT and Cogionis, B. (2000) Nucleated RBCs - Significance in the Peripheral Blood Film. Laboratory Medicine 31, 223-229.
4. Laroche, V., McKenna, DH, Moroff, G., Schierman, T., Kadidlo, D. and McCullough, J. (2005) Cell loss and recovery in umbilical cord blood processing: a comparison of postthaw and postwash samples Transfusion 45, 1909-1916.
5. Sigfusson, A. and Souhami, R. (1984) The Effects of Erythrocyte Contamination on Pokeweed Mitogen Induced Immunoglobulin-Synthesis in Man. Journal of Immunological Methods 72, 167-170.
6. Szabo, SE, Monroe, SL, Fiorino, S., Bitzan, J. and Loper, K. (2004) Evaluation of an Automated Instrument for Viability and Concentration Measurements of Cryopreserved Hematopoietic Cells. Laboratory Hematology 10, 109-111.
Fifth, use the instrument to publish an article
Author | Date | Title | Journal | Cell Type | Cellometer / Applications |
Mahato, Ram I | November 2013 | Synthesis and Characterization of an Anti-Apoptotic Immunosuppressive Compound for Improving the Outcome of Islet Transplantation | Bioconjugate Chemistry | PBMC | Cellometer Auto T4... Cell Counting |
Banerjee, Subhadra | October 2013 | Expression of the B-Cell Receptor Component CD79a on Immature Myeloid Cells Contributes to Their Tumor Promoting Effects | PLOS ONE | PBMC | Cellometer (Not Specified)... Cell Concentration |
Bogoslovsky, Tanya | September 2013 | Cryopreservation and Enumeration of Human Endothelial Progenitor and Endothelial Cells for Clinical Trials | Blood Disorders and Transfusion | PBMC | Cellometer Auto T4... Trypan Blue Exclusion |
Singh, Harjeet | May 2013 | Manufacture of Clincal-Grade CD-19-Specific T Cells Stably Expressing Chimeric Antigen Receptor Using Sleeping Beauty System and Artifical Antigen Presenting Cells | PLoS one | PBMC, Daudi, NALM-6, EL-4 | Cellometer Unspecfied... Trypan blue viability |
Shankar Pandey, Gouri | January 2013 | Detection of Intracellular Factor VIII Protein in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells by Flow Cytometry | BioMed Research International | PBMCs | Cellometer Unspecfied... Trypan blue viability |
Filbert, Helene | October 2012 | Serum-free freezing media support high cell quality and excellent ELISPOT assay performance across a wide variety of different assay protocols | Cancer Immunology and Immunotherapy | PBMC | Nexcelom Cellometer... Trypan blue viability |
Duran, MC | July 2012 | Enhanced protocol for CD14+ cell enrichment from equine peripheral blood via anti-human CD14 mAb and automated magnetic activated cell sorting | Equine Veterinary Journal | PBMCs | Cellometer Auto T4... Trypan blue viability |
O'Connor, Colleen M. | February 2012 | Adoptive T-cell therapy improves treatment of canine non-Hodgkin lymphoma post chemotherapy | Scientific Reports | T-cells and PBMC | Cellometer Auto T4... Trypan blue viability |
Clark, Eva H. | January 2012 | Plasmodium falciparum Malaria in the Peruvian Amazon, a Region of low Transmission, Is Associated with Immunologic Memory | Infection and Immunity | PBMC | Cellometer Auto T4... Trypan blue viability |
Sethu, Palaniappan | December 2011 | Clinical application of microfluidic leukocyte enrichment protocol in mild phenotype sickle cell disease (SCD) | Biomedical Microdevices | Leukocyte-enriched sample, PBMC | Cellometer (Not Specified)... Cell Number |
Uhl, Elizabeth | August 2011 | Identification of Altered MicroRNA Expression in Canine Lymphoid Cell Lines and Cases of B- and T-Cell Lymphomas | Genes, Chromosomes, & Cancer | GL-1; CL-1, LN, PBMC | Cellometer Auto T4... Other |
Lee, Moo-Seung | June 2011 | Shiga toxins induce autophagy leading to differential signalling pathways in toxin-sensitive and toxin resistant human cells | Cellular Microbiology | Primary PBMCs, THP-1 | Cellometer Automated Cell counter... Other |
Zierold, Claudia | May 2011 | Developing mechanistic insights into cardiovascular cell therapy: Cardiovascular Cell Therapy Research Network Biorepository Core Laboratory rationale | American Heart Journal | Bone Marrow, PBMC | Cellometer Auto T4... Trypan blue viability |
Pathak, Shresh | February 2011 | IL-1B; Is Overexpressed and Aberrantly Regulated in Corticosteroid Nonresponders with Autoimmune Inner Ear Disease | The Journal of Immunology | PBMC | Cellometer Auto T4... Trypan blue viability |
Wullner, Danika | June 2010 | Considerations for optimization and validation of an in vitro PBMC derived T cell assay for immunogenicity prediction of biotherapeutics | Clinical Immunology | PBMC, Dendritic, CD4 | Cellometer Auto T4... Trypan blue viability |
Bruchova, Hana | March 2009 | Erythropoiesis in polycythemia vera is hyper-proliferative and has accelerated maturation | Blood Cells, Molecules, and Diseases | PBMC | Cellometer Auto T4... Trypan blue viability |
Meyers, John A. | February 2009 | Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and B and T Cells Differ in their Response to Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors | The Journal of Immunology | CLL cells, PBMC | Cellometer Auto T4/M10... Normalizati |
White, William N. | December 2008 | Clinical application of microfluidic leukocyte enrichment protocol in mild phenotype sick cell disease (SCD) | Biomedical Microdevices | PBMC, PNM, Erythrocytes | Cellometer Auto T4... Other |
Bruchova, Hana | August 2007 | Regulated expression of microRNAs in normal and polycythemia vera erythropoiesis | Experimental Hematology | PBMC, JAK2 V617F | Cellometer Auto T4... Trypan blue viability |
Antigen Test Kit Of COVID-19
These test kits are new to the market and rely on the detection of viral proteins in swab samples They consist of monoclonal antibodies specific for the viral antigens and results are seen by the naked eye by way of chromatographic particles. There have only been a few of these tests commercialized and normally require a high viral count to work effectively. In the first few months of the pandemic some national health authorities questioned the reliability of these tests, as they usually require a higher viral count that qPCR to show positive. Therefore, false-negatives can occur.
antigen test kit, rapid antigen test kit, covid-19 antigen test, antigen detection, antigen rapid test kit
Shenzhen Uni-medica Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.unimed-global.com