The surgical robot is an intelligent service robot that can determine the operating procedure according to the actual situation according to the operation plan prepared by the doctor, and then forward the operating program into operable mechanical motion. The emergence of the Da Vinci robot heralds the advent of the third generation of surgical surgery.

The Da Vinci surgical robot is currently the most successful and widely used surgical robot in the world. It also represents the highest level of surgical robots today. It is mainly composed of three parts: 1. Doctor control system; 2. 3D imaging video imaging platform; 3. Robotic arm, camera arm and surgical instruments form a mobile platform.
During the operation, the surgeon does not directly contact the patient, and is operated and controlled by the three-dimensional vision system and the motion calibration system. The mechanical movement and the surgical operation are completed by the robot arm and the surgical instrument simulation.
Four generations of products have been developed to date: the first generation was the Da Vinci standard surgical robot system, which was commercialized in 1999. The second generation was the Da Vinci S surgical robot system, which was commercialized in 2006. The third generation is the Da Vinci Si Surgery Robot System, which was commercialized in 2009. The fourth generation is the Da Vinci Xi Surgery Robot System, which was released in the second quarter of 2014.
At present, Da VinCi surgical robots are widely used in general surgery, urology, cardiovascular surgery, thoracic surgery, gynecology, ENT, pediatric surgery.

For decades, the development of minimally invasive surgical techniques has revolutionized the development of surgical procedures, and the endoscopic surgical robots based on Da Vinci surgical robots have further broadened the scope of minimally invasive surgery and led The high-tech and cutting-edge level of minimally invasive surgery. The Da Vinci surgical robot is the only intelligent endoscopic minimally invasive surgery system approved by the FDA (US Food and Drug Administration) for surgical clinical treatment.
World use
The market for Da Vinci surgical robots is still dominated by the US domestic market, with revenue accounting for more than 70%.
In the United States, Da Vinci robots have become very popular. In more than 5,000 hospitals including community hospitals, the installed capacity of Da Vinci robots has reached more than 2,200. As long as it is a large-scale hospital, it will definitely be equipped. Finch robot.

In the United States, Da Vinci robots have become very popular. In more than 5,000 hospitals including community hospitals, the installed capacity of Da Vinci robots has reached more than 2,200. As long as it is a large-scale hospital, it will definitely be equipped. Finch robot.
As of 2014, Intuition Surgery has sold 3,266 Da Vinci surgical robot systems, including 2,254 in the US, 556 in Europe, 191 in Japan, and 301 in other regions. Since the cumulative sales volume has exceeded 1,000 units in 2008, it has maintained rapid growth for several consecutive years. However, since 2013, the growth rate has slowed down. In 2013, the global installed capacity of Da Vinci robots reached 2,966 units, and in 2014, it reached 3,266 units, with a growth rate of 10.1. %.
Da Vinci in China
The only agent of Da Vinci Robots in China is the US-China Mutual Company.
Since the introduction of the first Da Vinci surgical robot in the General Hospital of the People's Liberation Army in 2006, the Da Vinci robot has entered China for ten years. However, since the Da Vinci surgical robot belongs to Class A large-scale medical equipment, the introduction of this equipment by any hospital in China requires direct approval by the Health Planning Commission, so the introduction speed has been slow. Since the introduction of the first Da Vinci robot in 2006, China the current total installed capacity of less than 40 mainland can also be seen from the number of da Vinci robot from the side of the high and low medical standards throughout the country.
Application of Da Vinci surgical robot in China

In 2013, there were 14 hospitals equipped with Da Vinci surgical robots in China (excluding Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan), and 18 Da Vinci surgical robots were deployed, including 4 local level A general hospitals: Huadong Hospital affiliated to Fudan University. , Ruijin Hospital affiliated to Shanghai Jiaotong University, Zhongshan Hospital affiliated to Fudan University, Peking Union Medical College Hospital; 2 local level A special hospitals: Beijing Ditan Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University Affiliated Chest Hospital; 7 military grade A general hospitals : Beijing Chinese People's Liberation Army General Hospital, Beijing People's Liberation Army Second Artillery General Hospital, Southwest Military Hospital affiliated to the Third Military Medical University, Nanjing General Hospital of Nanjing Military Region, Shenyang Military Region General Hospital, Changhai Hospital affiliated to the Second Military Medical University, Jinan Military Region General Hospital, Xijing Hospital affiliated to the Fourth Military Medical University. Among them, the Beijing PLA General Hospital has a total of 5 Da Vinci surgical robots, and one in each hospital.
In 2014, the Health and Family Planning Commission approved 11 new public hospitals equipped with surgical robots, all of which were Da Vinci.
These 11 hospitals are:
Jilin Provincial Cancer Hospital
Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine
Nanjing Gulou Hospital
First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine
Zhejiang People's Hospital
The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University
The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University
Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University Medical College
First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University
First Affiliated Hospital of Zhongshan University
Sichuan Provincial People's Hospital
In 2015, Tongji Hospital and Union Hospital in Hubei, Xiangya Second Hospital in Hunan, and Xiangya Third Hospital were approved for the deployment of surgical robots. It is worth noting that the Xiangya Third Hospital has the first domestically produced surgical robot in China.
Clinical application level of domestic Da Vinci surgical robot
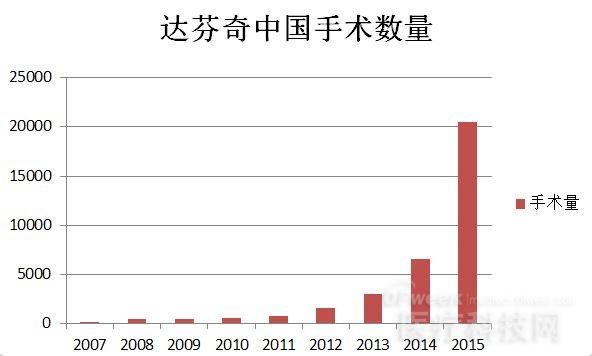
In China, the hospital equipped with Da Vinci surgical robots completed 2,984 Da Vinci robotic operations in 2013. In 2012, 1546 cases were completed. In 2011, 808 cases were completed. The annual operation volume increased by 91% for two consecutive years. By the end of 2014, there were 6,535 cases of Da Vinci robotic surgery completed in the past years.
As of October 2015, a total of 20,477 Da Vinci robotic surgeries have been completed throughout the country.
The number of hospital operations in the past years (more than a thousand cases):
4215 cases of PLA General Hospital
1626 cases of Shanghai Zhongshan Hospital
1605 cases of Nanjing General Hospital of Nanjing Military Region
1530 cases of Chongqing Southwest Hospital
Xi'an Xijing Hospital 1360 cases
1335 cases of Shanghai Ruijin Hospital
1006 cases of Shanghai Changhai Hospital
Real experience: What does it feel like to operate Da Vinci?
First of all, there is no such requirement in foreign countries, but in China, the Da Vinci robot is required to be certified. This certificate is a training certificate of the intuitive company. The training content is divided into several stages. The most basic training is very simple. It takes 2 days and has an assessment after the end. There is no training base in the mainland. The most recent training base is in Hong Kong University, Prince of Wales Hospital, Jockey Club Robot Training Center. After the general hospital determines the purchase, the US-China Mutual Company will be responsible for contacting the other side, and then the hospital will send a team of doctors and nurses to receive training.
Then, the very intuitive feeling is: Big Mac! No wonder a special large operating room is needed. The console is usually placed in a small room next door and is not small. The two are connected by cables.
The robot arm is a high-value consumable. It is temporarily installed on the robot during use. Each arm has a limit on the number of uses, and it cannot be used after 10 times. The price of the robotic arm is about $100,000 per piece. On average, each operation requires at least 4 arms, so the startup cost is about 4-6 million.
The robotic arm is the core component here. It looks like a laparoscopic instrument. It has universal arms, grippers, scissors and other different arms. The positions are interchangeable. Unlike laparoscopic instruments, each arm has a number of small joints that can perform a variety of complex tasks that are sometimes impossible to perform with human hands. The robot's laparoscope is very large and is also mounted on a dedicated arm.
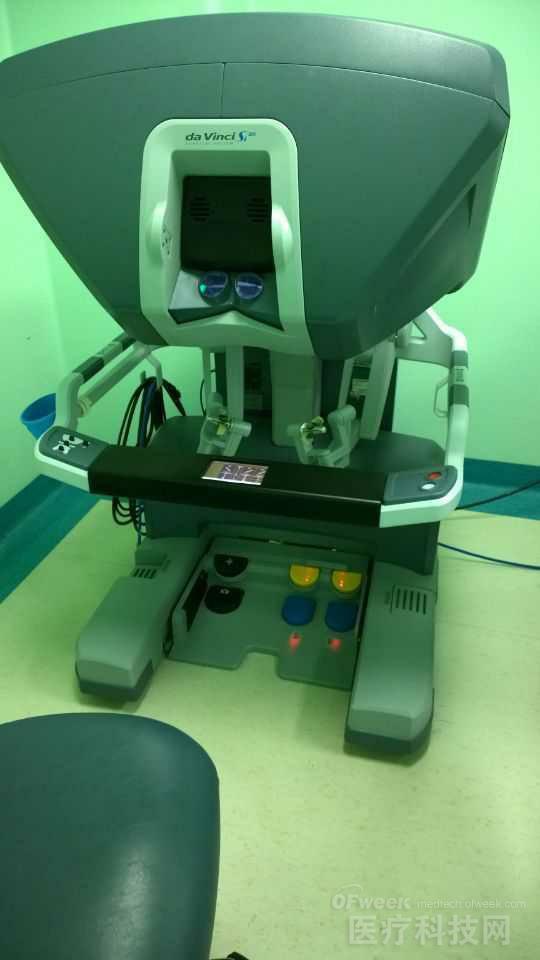
This picture is a real shot of the center console. (A new type of machine, one robot can connect two center consoles, and operate four robot arms at the same time. So if you buy 2 central control, then in theory, you can actually operate the robot arm at the same time. However, the problem with this is that the surgeon and the helper need to cooperate, otherwise the robotic arm is very dangerous in the body. Therefore, the actual operation is one person. Only one of the hospitals I have visited is a robot. 2 center consoles, others like us, 1 to 1)
The operator is sitting in a chair and looking directly at the eyepiece. Because the laparoscope itself is a double lens, with the view of the dual objective lens, the 3D display of the Da Vinci robot is very realistic, the stereoscopic effect and the layering are very good, and the accurate spatial distance can be obtained.
The baffle on the support arm has a small LED display that shows basic information such as the patient, the surgeon, and the procedure. The front is the operating lever, the finger is placed on the top to operate, can control the two arms at the same time, carry out various operations such as moving, cutting, hemostasis, suturing, knotting, etc., the sensitivity is not inferior.
Next is the foot pedal below, the black control on the left side moves the laparoscopic robot arm in various orientations. The right side is the same as the pedal of a normal electric knife. It is yellow cut and blue to stop bleeding.
The operating experience is first and foremost comfortable. Sitting on the surgery, and the arm is supported, completely eliminating the fatigue of laparoscopic surgery.
Secondly, the 3D effect is good, just like the human eye is direct, there is a sense of distance, the operation is natural and accurate, and the distance is determined according to the deformation of the object in the field of vision combined with the experience of the surgeon in the laparoscopic surgery.
Once again, the robotic arm is flexible enough, like a human hand, with 13 joints, which can perform a variety of complex movements. It also has anti-shake function, so there are also cardiac surgeons who use it for coronary artery bypass. Such complicated and dangerous surgery as thrombectomy with a vena cava grade 4 tumor thrombus can be performed under robotic laparoscopy.
Finally, the feedback rate is very high and the delay is very weak. The 7+1 degree of freedom is a good fit for operational needs, and the range of activities is much less restrictive than the human hand. It can be used to make a lot of movements that are not possible on the wrist. Because it links the movement of the tool head and the wrist, it can achieve the action that can not be done by directly holding the surgical instrument. (For example, the end of the pliers head can be freely rotated in the Rx.Ry.Rz direction, instead of being restricted by the pliers handle like a hand held pliers.) The reconstruction of the three-dimensional vision by both eyes is very good, and the person can adapt intuitively and without obstacles.
From the United States to China, the road is long and far-reaching.
Although the world market continues to recognize surgical robots, in China, the penetration rate and penetration rate of surgical robots have been low due to long certification times and expensive use. From the perspective of certification, most foreign research institutions adopt the management mode of enterprises. All the links in R&D, market and certification have special teams to follow up, with clear division of labor and high efficiency. However, in China, most of the R&D teams have the task of certification, and they are powerless for the cumbersome certification process. Surgical robots belong to Class A large-scale medical equipment and need to be reported to the health administrative department of the State Council for review. It takes about 3-5 years for a product to go from research and development to the stage.
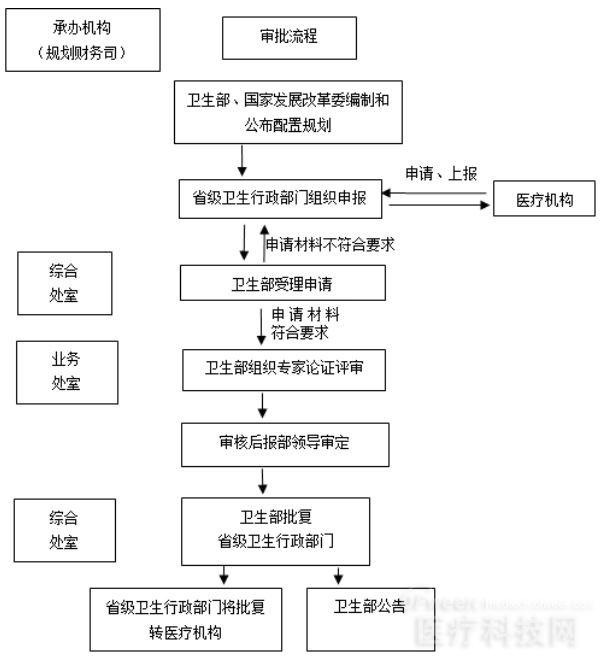
Source: Ministry of Health, A large-scale medical equipment allocation approval system
In addition, from the price point of view, the domestic price of Da Vinci's latest generation system is around 25 million. In addition to the host fee, it also includes taxes, training fees, and clinical technical support fees. If the cost is distributed to each operation, the cost of robotic surgery is about 30,000 yuan higher than the cost of traditional surgery. In addition, the cost of surgery based on Da Vinci robots has not been included in the national medical insurance reimbursement scope, resulting in limited application of robotic surgery.
Although the Da Vinci surgical robot combines many disciplines such as medicine, biomechanics, mechanics, mechanics, materials science, computer graphics, computer vision, artificial intelligence, mathematical analysis, robotics, etc., it is not foolproof, using surgical robots to do Surgery still has certain risks, and medical disputes are still difficult to avoid.
With the popularity of Da Vinci surgical robots, more and more experts and scholars are beginning to worry about the safety and effectiveness of this technology. Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, MIT, and Rush University reported in a publicly available pre-printed website that between 2000 and 2013, surgical robots “killed†144 patients, causing 1,391 patients to be injured. 8061 mechanical failures occurred
In general, under the current saturation of the US market, if the Intuition Surgery Company (ISGR) can not successfully win new markets such as Europe and China, its development will encounter considerable obstacles for 2016. Performance, we will wait and see.
surgical gown,non steril isolation gown,sms gown,white gown,blue gown
Shandong Zhushi Pharmaceutical Group Co.,LTD , https://www.sdzs-medical.com